

Treatment with different antibiotics will usually solve this problem. This condition is usually caused by chlamydia that didn't respond to an earlier treatment. Men can suffer from postgonococcal urethritis (inflammation of the urethra, the tube running down the centre of the penis). Symptoms sometimes remain for a while after treatment. All people treated for gonorrhea will need to follow up with their doctor in 6 months. It is very important to take medications exactly as prescribed, and some people will require a follow-up test after finishing treatment.
Ask your doctor how long you should wait before beginning sexual contact again after the treatment.įluoroquinolones, penicillins, or tetracyclines used to be effective therapies, but many of the strains today have developed resistance to these antibiotics. People with gonorrhea often have chlamydia, and this treatment treats chlamydia as well.
#LONG TERM GONORRHEA SYMPTOMS PLUS#
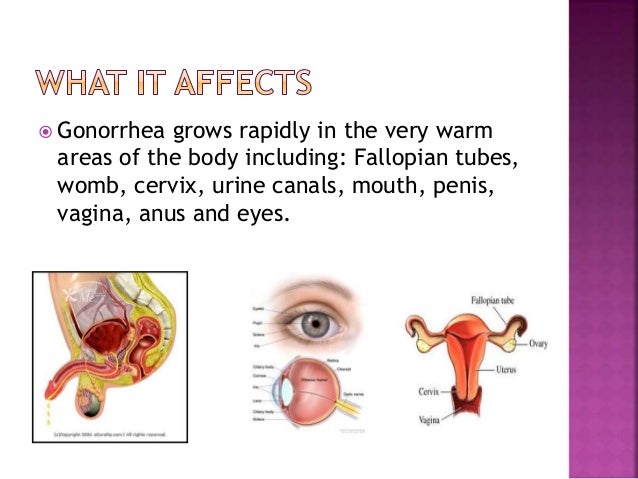
In uncomplicated cases, the usual treatment is a single dose of a medication such as ceftriaxone* injected into the muscle, or cefixime, a pill, plus a dose of oral azithromycin. A variety of treatments are available for gonorrhea. Some people with gonorrhea have symptoms involving the rectum such as itching and discharge or possibly painful bowel movements. Gonorrhea in the eyes is serious – it can cause blindness if left untreated. Gonorrhea of the throat usually has no symptoms but sometimes causes a sore throat and difficulty swallowing. They can cause inflammation and pain in the joints ( arthritis) and liver ( perihepatitis) and a potentially serious infection of the heart valves ( endocarditis). Other complications of gonorrhea occur when the bacteria get into the bloodstream. The main complication in men is epididymitis (inflammation of the part of the testicles where sperm is stored), which can cause infertility if not treated. Symptoms of PID include pelvic pain, fever, abdominal tenderness, and vaginal discharge. The result is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which occurs in up to 20% of women with gonorrhea and can cause infertility. Left untreated, gonorrhea can work its way up the urethra and cervix to other pelvic organs. While women feel fewer symptoms, they are far more vulnerable to serious complications of gonorrhea. Most women are diagnosed only when their partner seeks treatment. The discharge is usually yellow or green, but it may also contain blood. A few have a noticeable vaginal discharge, which may actually be coming from the cervix. Most women don't have symptoms unless there are complications. The opening of the penis may be red and swollen. Urinating often causes burning pain that can be severe. In men, there is a discharge of yellow or greenish pus from the penis and a frequent need to urinate. The first symptoms typically appear after 2 to 7 days but occasionally appear months after infection. Gonorrhea is far more likely to cause symptoms in men than in women.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
